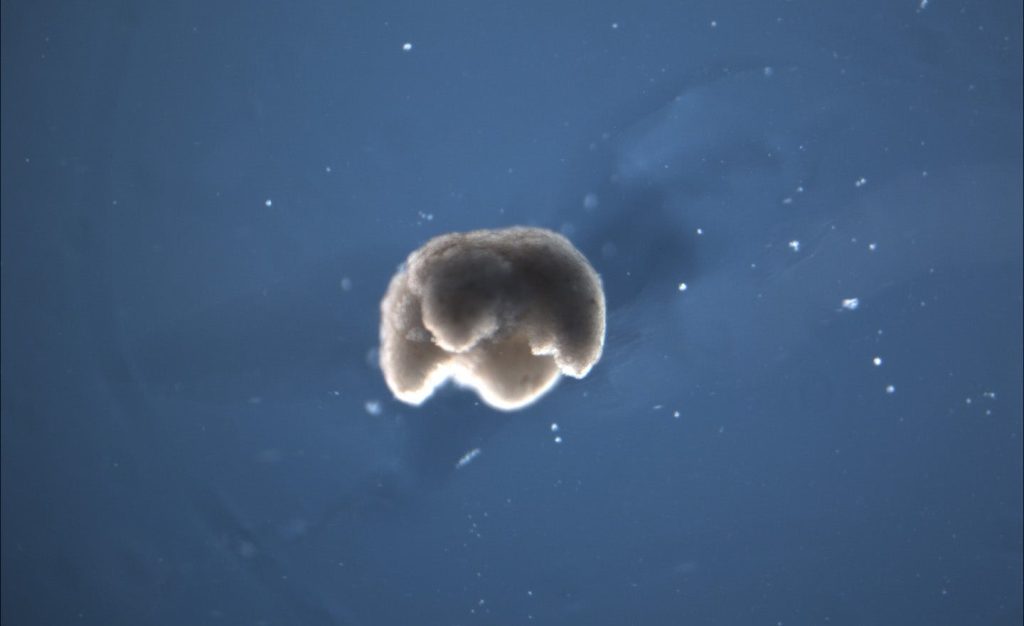
The scientists who created xenobots, the world’s first living robots, say the lifeforms are “the first self-replicating living robots”.
They were microorganisms Originally revealed In 2020, the robots will consist of stem cells from the heart and skin of the African clawed frog. They can move around on their own for about a week before they run out of energy, repairing and decomposing themselves naturally.
Scientists from the University of Vermont, Tufts University and Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering published research Monday in which they said they had discovered a new biological species, unlike any other known plant or animal species, according to a press release. published by The Wyss Institute.
“People have long believed that we figured out all the ways that life can reproduce or reproduce, but that’s something we haven’t seen before,” said Douglas Blackstone, PhD, a senior scientist at Tufts University. The university and the Wyss Institute who participated in the study.
Scientists say the new research could prove useful in terms of medical use.
“If we knew how to tell cell groups to do what we wanted them to do, then this is the ultimate regenerative medicine — this is the answer to trauma, birth defects, cancer and ageing,” Michael LevineMichael (Mike) Ted Levine California’s proposed mapping puts incumbents at risk for a ban on new offshore drilling that must remain in the Build Back Better Act., Ph.D., co-leader of research. All of these different problems exist because we don’t know how to predict and control the populations of cells that you’re going to build. Xenobots is a new platform for our education.”

“travel. naughty. Pop culture fanatics. I can’t write with boxing gloves on.”

“Lifelong entrepreneur. Total writer. Internet ninja. Analyst. Friendly music enthusiast.”










More Stories
Monster Jam Showdown Launch Trailer
The European Digital Twin Ocean prototype reveals many possibilities
Instagram now lets you add a song to your account