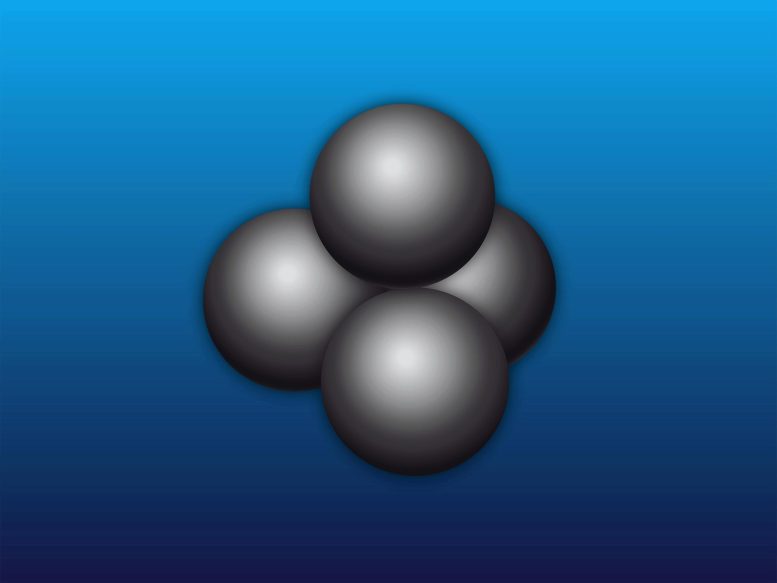
The experiment using four neutrons found evidence of a long-sought particle consisting of four neutrons.
While all atomic nuclei except hydrogen are made up of protons and neutrons, physicists have been searching for a particle with one, three, or four neutrons for more than half a century. Experiments conducted by a team of physicists from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) in the accelerator lab on the Garching research campus indicate the possibility of a particle with four bound neutrons.
While nuclear physicists agree that there are no only proton systems in the universe, they have been searching for particles with one, three or four neutrons for more than 50 years.
At the Van de Graaff tandem accelerator at the Maier-Leibnitz Laboratory on the Garching Research Campus, a team of physicists from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) bombarded a lithium-7 target with a lithium-7 atomic nucleus accelerating to 12 percent the speed of light. All measurement results indicate that their experiments yielded the desired carbon-10 and tetratron. Credit: Sonja Battenberg / TUM
If such a particle exists, parts of the theory of the strong interaction must be reconsidered. In addition, studying these particles more closely can help us better understand the properties of neutron stars.
“A strong interaction is literally the force that holds the world at its core. Atoms heavier than hydrogen would be unimaginable without them,” said Dr. Thomas Westermann, who led the experiments.
Everything now points to the fact that it is precisely these types of particles that originated in one of the recent experiments on Van de Graaf’s now-defunct tandem particle accelerator at the Garching research campus.
At the Van de Graaff tandem accelerator at the Maier-Leibnitz Laboratory on the Garching Research Campus, a team of physicists from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) bombarded a lithium-7 target with a lithium-7 atomic nucleus, accelerating to 12. percent of the speed the light. All measurement results indicate that their experiments yielded the desired carbon-10 and tetratron. Credit: Thomas Faestermann / TUM
The long search for a tetratron
Twenty years ago, a French research group published measurements that they interpreted as a signature of the desired tetraneutron. However, subsequent work by other groups showed that the method used could not prove the existence of a tetratron.
In 2016, a group in Japan attempted to make a tetratron out of helium-4 by bombarding it with a beam of radioactive helium-8 particles. This reaction should produce beryllium-8. In fact, they were able to detect four such atoms. From the measurement results, the researchers concluded that the tetraneutron was uncorrelated and quickly returned to four neutrons.
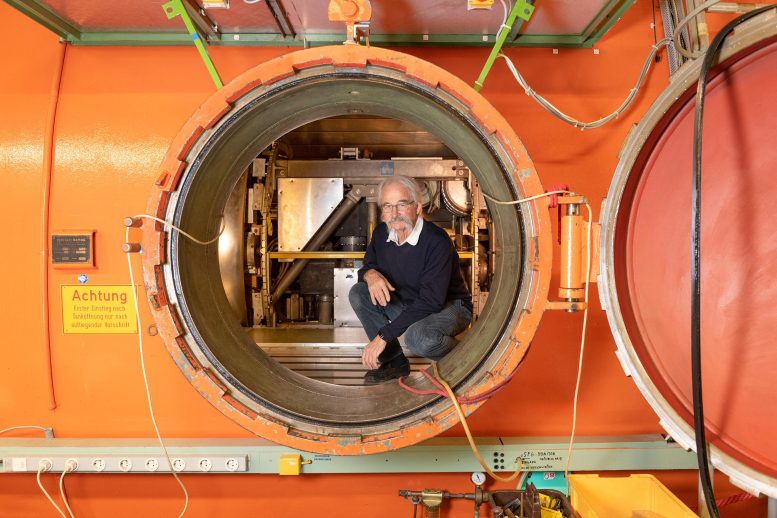

Doctor. Thomas Westermann in the Van de Graaff accelerator access hatch alongside the Garching research campus. Here, more than ten million volts of lithium ions are accelerated to about 12 percent of the speed of light. Westerman and his team fired at a lithium-7 target using lithium ions. All measurement results indicate that their experiments yielded the desired carbon-10 and tetratron. Credit: Ole Benz / TUM
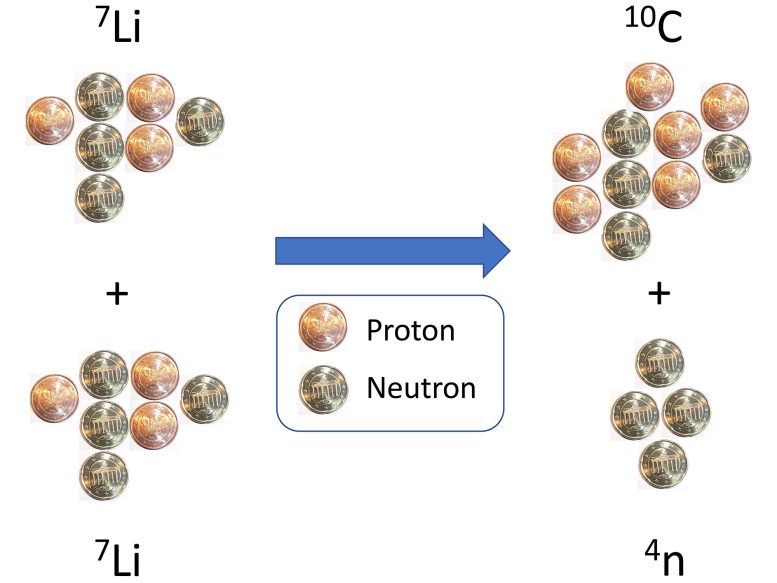
In their experiments, Westerman and his team bombarded a lithium-7 target with lithium-7 particles that accelerated to about 12 percent the speed of light. In addition to the tetratron, carbon 10 should be produced. Already, physicists managed to discover this species. Repetition confirmed the result.
circumstantial evidence
The team’s measurements matched the expected signature of carbon 10 in its first excited state and a bound tetratron of 0.42 megaelectronvolts (MeV). According to the measurements, the tetratron will be as stable as the neutron itself. It then degrades through beta decay with a half-life of 450 seconds. “For us, this is the only plausible physical explanation for the measured values in all respects,” explains Dr. Thomas Westerman.
Doctor. Roman Gernhauser, a researcher in the Department of Physics at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), is in the target room of the Van de Graaff tandem accelerator on the Garching campus, where lithium ions are accelerated to about 12 percent the speed of light, the purpose of lithium 7. All measurement results indicate that Their experiments produced the desired carbon-10 and tetratron. Credit: Ole Benz / TUM
From their measurements, the team achieved a certainty of more than 99.7 percent, or 3 sigma. But in physics, the existence of a particle is not considered final until 5 sigma certainty is reached. Therefore, researchers are now eagerly awaiting independent confirmation.
Reference: “Indicators for a Coupled Quadrivalent Neutron” By Thomas Westermann, Andreas Bergmayer, Roman Gernhauser, Dominic Kohl and Mahmoud Mahgoub, 26 Nov 2021 Available here. Physics Letters B.
DOI: 10.1016 / j.physletb.2021.136799
The Mayer-Leibnitz Laboratory, with the Van de Graaf tandem accelerator, is jointly operated by the Technical University of Munich and Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. The facility closed in early 2020 for structural reasons. All five authors of the publication are graduates or employees of the Technical University of Munich.

“Lifelong entrepreneur. Total writer. Internet ninja. Analyst. Friendly music enthusiast.”











More Stories
Monster Jam Showdown Launch Trailer
The European Digital Twin Ocean prototype reveals many possibilities
Instagram now lets you add a song to your account